ISO 25239: The essential standard for Friction Stir Welding of Aluminium
Aluminium is a key material in many industries, ranging from aerospace and automotive to shipbuilding. Among the various welding methods available, Friction Stir Welding has emerged as a revolutionary technique, offering high-quality welds with exceptional structural integrity. The ISO 25239 standard was specifically developed to regulate and standardize this innovative process. This standard plays a crucial role in defining clear guidelines and stringent requirements for the assembly of aluminium by FSW, thereby ensuring optimal performance and increased safety. Whether you are an engineer, a manufacturer, or a quality professional, this article will provide you with the essential knowledge to effectively adopt and apply the ISO 25239 standard in your aluminium FSW welding operations.
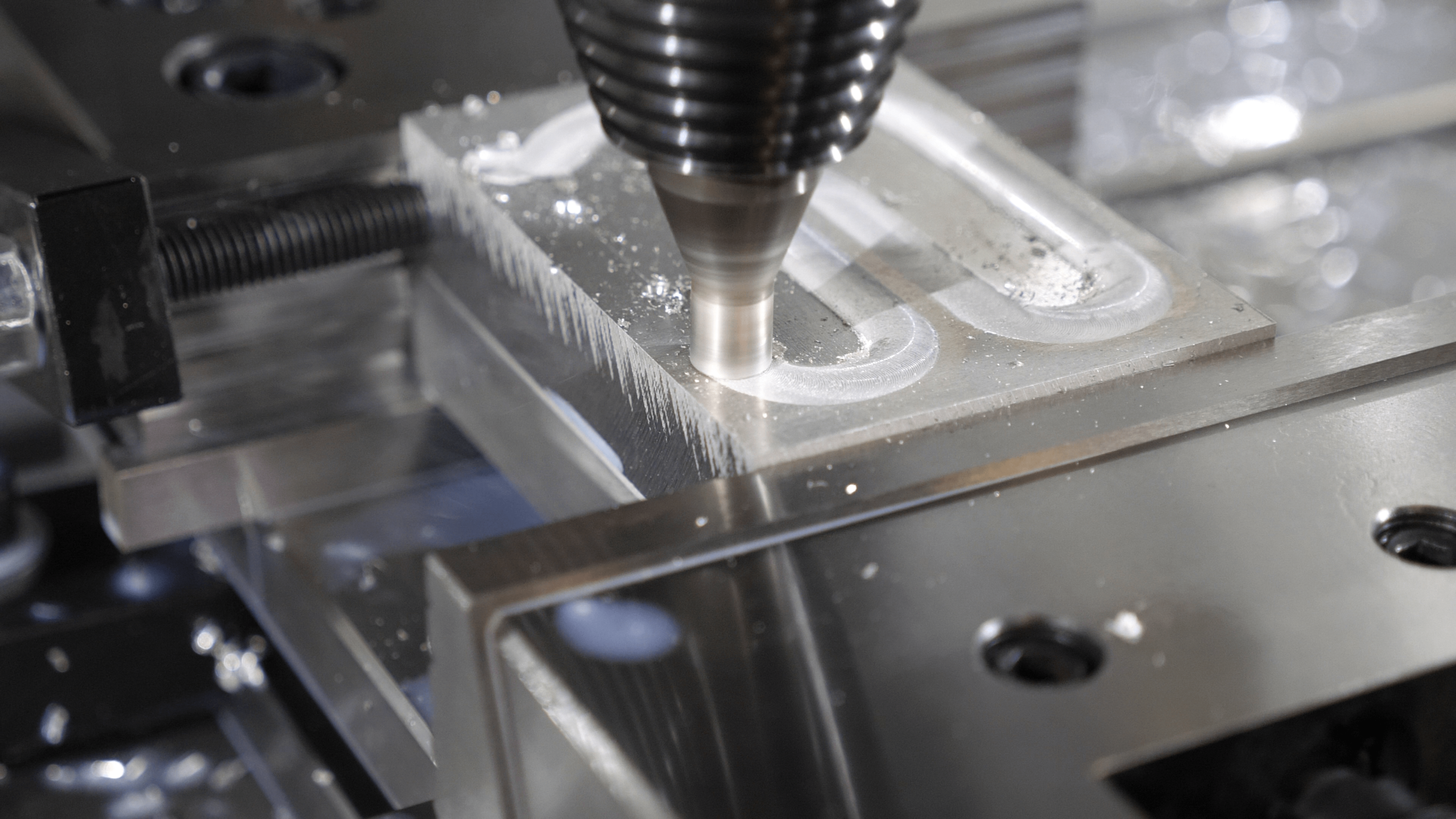

Fundamentals of Friction Stir Welding: 4 Criteria to Achieving Quality Welds
To achieve a high-quality weld, it is essential to consider four specific criteria:
By considering these four criteria, you can optimize your FSW processes and guarantee quality welds according to the ISO 25239 standard.
ISO 25239: the Essential Standard for Reliable and Compliant FSW Welds
The ISO standard was developed to provide comprehensive guidelines and specific technical requirements for the FSW of aluminium.
Main objectives of the standard
The main objectives of ISO 25239 are:
Structure and content of ISO 25239
ISO 25239 is divided into several parts, each covering a specific aspect of the Friction Stir Welding process. Here are the main sections of the standard:
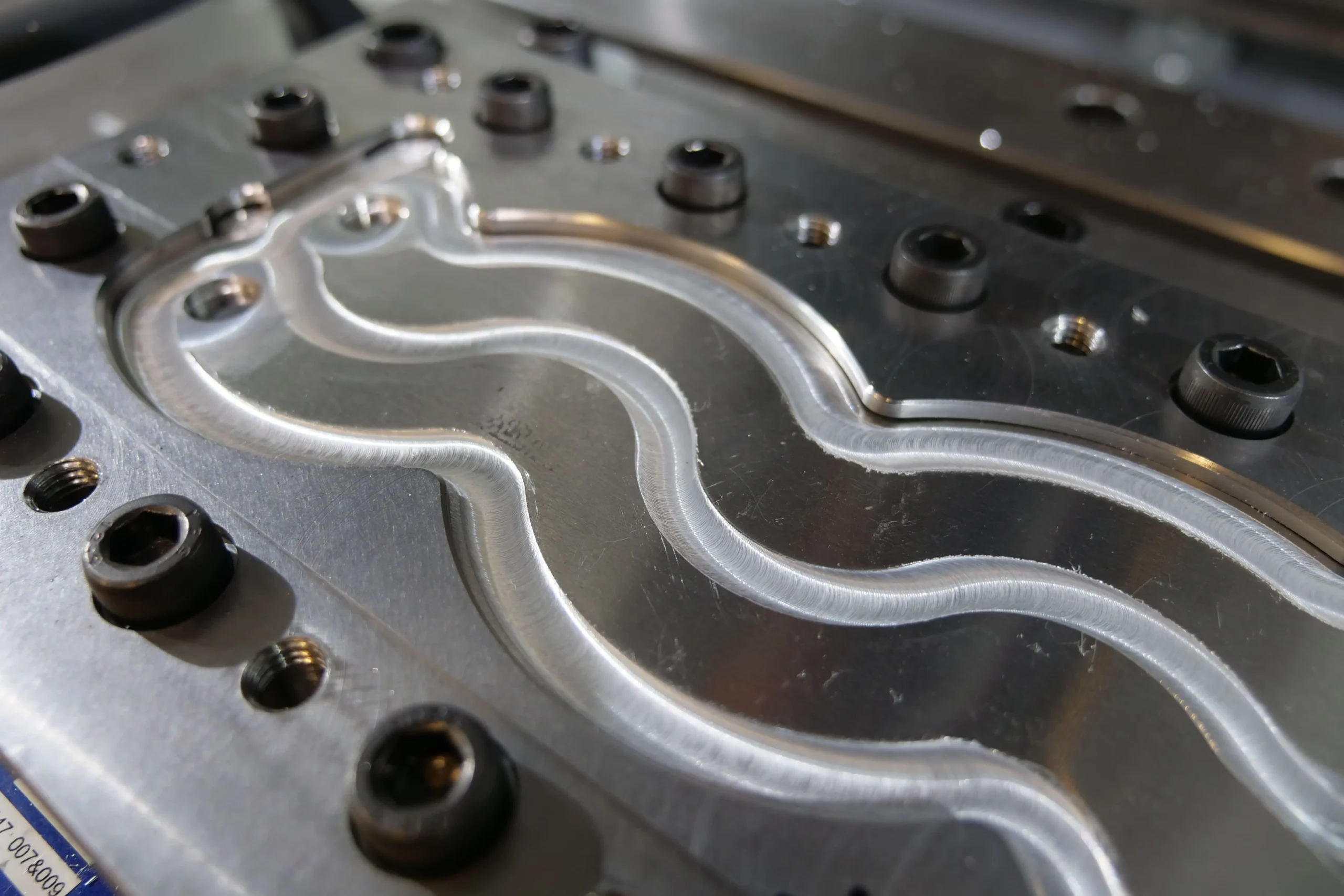

Impacts and benefits of the standard
Adopting ISO 25239 brings numerous significant advantages to companies. Firstly, it leads to a notable improvement in weld quality. By following clear and precise guidelines, companies can produce more reliable and durable welds, reducing the risks of defects and rework. This standardization of Friction Stir Welding process also results in substantial cost savings by reducing the expenses associated with rework and welding failures.
Additionally, ISO 25239 helps company comply with legal and industrial requirements. By adhering to these standards, they can more easily obtain the necessary certifications, facilitating access to new markets and ensuring essential regulatory compliance. This compliance enhances the credibility and trust of customers and business partners.
Furthermore, adopting ISO 25239 allows companies to increase their competitiveness in the global market. By adopting internationally recognized welding practices, they can demonstrate their commitment to quality and innovation, thereby differentiating themselves from the competition.
In summary, ISO 25239 represents a strategic tool for improving weld quality, optimizing production costs, ensuring regulatory compliance, and strengthening the competitive position of companies in the global market.
Technical and Quality Requirements
The ISO 25239 standard defines rigorous technical requirements and quality criteria for Friction Stir Welding of aluminium:
Technical Specifications
Quality Criteria

Tests and Certifications
By following these requirements, companies can ensure high-quality FSW welds that meet international standards, ensuring the safety and durability of welded structures.
Why Adopted the ISO 25239 Standard?
Adopting the ISO 25239 standard offers numerous advantages for companies using the FSW process.
Improved Weld Quality
One of the most significant advantages of adopting the ISO 25239 standard is the improvement in weld quality. By following the standard’s clear and precise guidelines, companies can ensure stronger and more durable welds, thereby minimizing the risk of failure. The strict quality criteria and technical requirements ensure that each weld meets the highest standards, reducing the need for rework and post-weld adjustments.
Reduced Production Costs
Standardizing FSW processes leads to significant production cost reductions. By minimizing welding defects and rework, companies can save on materials, labor, and time. Moreover, using optimized welding parameters and suitable equipment increases operational efficiency, reducing downtime and increasing overall productivity.
Regulatory Compliance and Increased Competitiveness
Adopting the ISO 25239 standard helps companies comply with regulatory and industry requirements. Conformance to this international standard is often a prerequisite for obtaining necessary certifications and accreditations, facilitating access to new markets and customers. By demonstrating their commitment to quality and best practices, companies can enhance their reputation and competitive position.
Innovation and Continuous Development
The adoption of the ISO 25239 standard also encourages innovation and continuous development. By following standardized practices and integrating the latest technological advancements, companies can stay at the forefront of progress in the FSW field. This proactive approach fosters continuous improvement in processes and products, enabling companies to meet changing market and customer demands.
In Which Sectors Is the ISO 25239 Standard Essential?
The ISO 25239 standard is essential in sectors using FSW, particularly for aluminium assembly. This certification is crucial in industries where welding requirements are particularly high:
- Automotive Industry: FSW is used for manufacturing body parts, chassis, battery trays, heat exchangers, and other components requiring lightness and robutness. This is particularly relevant in e-mobility, where ISO 25239 certification ensures the quality and safety of components.
- Railway Industry: FSW is used to assemble components of trains, wagons, subways, and more.
- Shipbuilding: Ship hulls, bridge structures, and other maritime components benefit from the ISO 25239 standard.
- Aerospace Sector: This sector widely uses FSW to manufacture lightweight and strong components. ISO 25239 certification is essential to ensure the reliability of parts subjected to significant stresses.
- Vacuum Industry: Achieving reliable vacuum seals is simplified with FSW, but quality standards are extremely high in this sector, making ISO 25239 certification essential for qualifying vacuum industry parts.
The ISO 25239 standard represents a significant advancement for the FSW industry. By offering clear guidelines and stringent technical requirements, this standard ensures high-quality, reliable, and compliant welds. Its adoption not only improves weld quality but also reduces production costs, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances workplace safety. Furthermore, it encourages innovation and continuous development, enabling companies to remain competitive.
To effectively integrate the ISO 25239 standard into your welding operations and reap its numerous benefits, it is essential to follow the implementation steps described and draw inspiration from best practices and successful case studies.

Ready to improve your welding operations and adopt the ISO 25239 standard
Contact us today for personalized advice and discover how we can help you implement this standard.

