Overcoming cold plate manufacturing challenges
The cold plate manufacturing industry is continuously advancing, prioritizing efficiency and innovation. However, even with these advancements, the sector grapples with several challenges — from potential leaks that threaten entire liquid cooling systems, and the urgent need to enhance thermal management efficiency, to the imperative to drastically cutting costs in a fiercely competitive marketplace, and ensuring the resilience of cold plates in extreme temperature conditions.
How can the industry address these challenges while continuing its trajectory of progress and delivering high-performance cooling solutions?
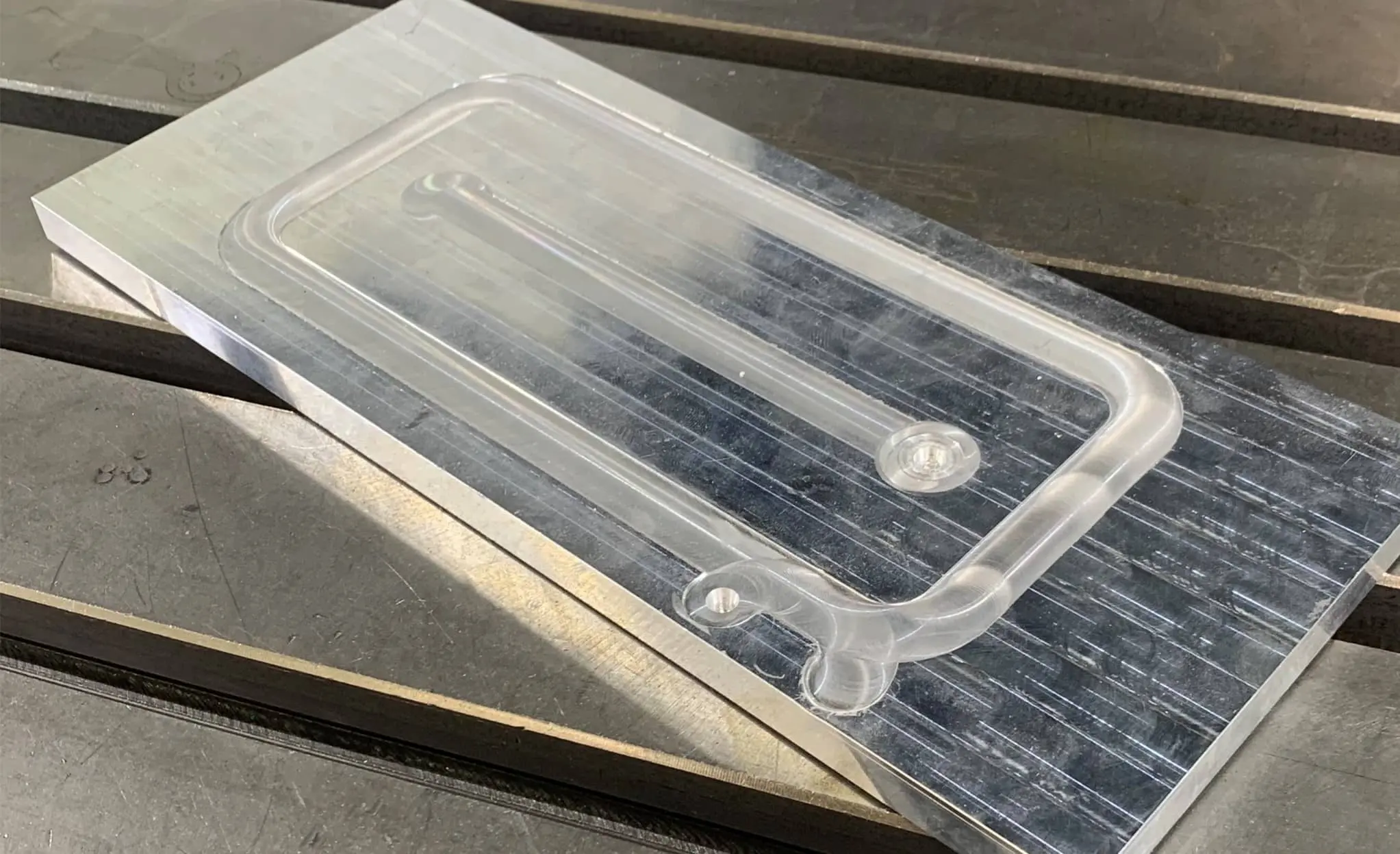

Understanding the pain points of liquid cold plate
Leak risks in cold plate manufacturing
The cold plate manufacturing industry grapples with critical challenges, notably the risk of leaks. Even minor leaks can severely disrupt liquid cooling systems,affecting coolant or fluid flow, leading to operational issues, escalating repair costs, and potential long-term damage to a company’s reputation — especially in sectors where reliable thermal management is vital.
Liquid cold plate strength
Parallel to this issue is the matter of cold plate strength. Strength is crucial in the demanding environments where liquid cold plates are used, especially to maintain consistent thermal performance under pressure.
Manufacturers aim to ensure longevity by enhancing this strength, often requiring more durable and expensive materials or techniques. The dilemma lies in balancing durability, high performance, and cost — without compromising thermal reliability.
Large liquid cold plate welded by FSW: 500 x 500 x 60 mm
Welding time: 10 min
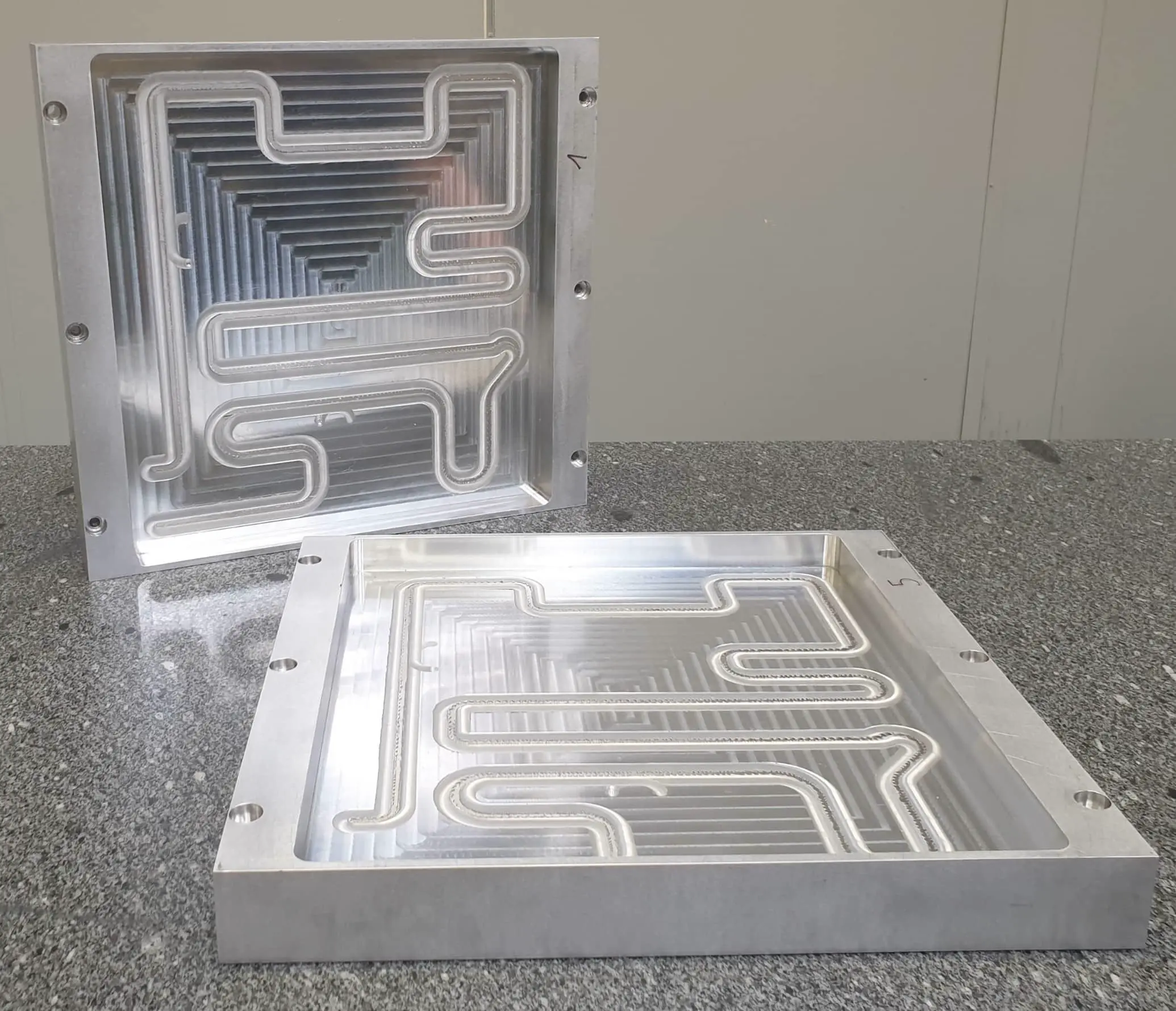
Large liquid cold plate welded by FSW: 500 x 500 x 60 mm
Welding time: 10 min
Improving thermal management in cold plate

Thin liquid cold plate: total thickness of 3 mm with lap welding of three 1 mm aluminium sheets in one step.
Welding time: 2 min
Thermal management is pivotal as the demand for high-performance batteries and energy efficiency rises. While the industry aims to double cold plate thermal performance, the challenge is to meet this target without significantly raising costs, increasing thermal resistance, or complicating the design and production process.
Cold plate production costs
In cold plate manufacturing, the pressing need for cost reduction stands out. Achieving a tenfold decrease requires major innovations in cold plate design, material choices — such as copper, aluminium or steel — production methods, and a comprehensive overhaul of the liquid cooling supply chain.
Improving every stage of the liquid cold plate process — from flow path optimization to the integration of heat exchangers and modular assembly components — is essential for reducing costs while maintaining high-performance standards.
Each highlighted issue is intricate on its own. Yet, when viewed together, they necessitate a comprehensive, unified strategy. In the upcoming sections, we will explore various cold plates and how the innovative method of friction stir welding can efficiently tackle these problems — from leak prevention to optimal heat transfer and streamlined cooling system integration.
Typical types of cold plates: overview and specific challenges
Cold plates come in various designs tailored to specific uses. Their manufacturing method, chosen materials — such as copper or aluminium — and overall cold plate design largely shape their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific applications. In this section, we will examine prevalent liquid cold plate types, pinpointing their unique characteristics and the challenges they face — such as managing heat loads, optimizing the flow path, or ensuring compatibility with complex cooling systems used in electronics, data centers, or laboratory environments.
Tube liquid cold plate
Tube liquid cold plates face challenges due to their design, limiting high channel density and, consequently, cooling performance. The manufacturing process, involving tube bending, thermal paste application, and hydroforming, can affect reliability if not done precisely. Moreover, joining copper tubes to aluminum plates risks bimetallic corrosion, affecting efficiency and plate durability, especially in harsh conditions. This emphasizes the need for innovations in tube liquid cold plate design and production to boost performance and reliability.
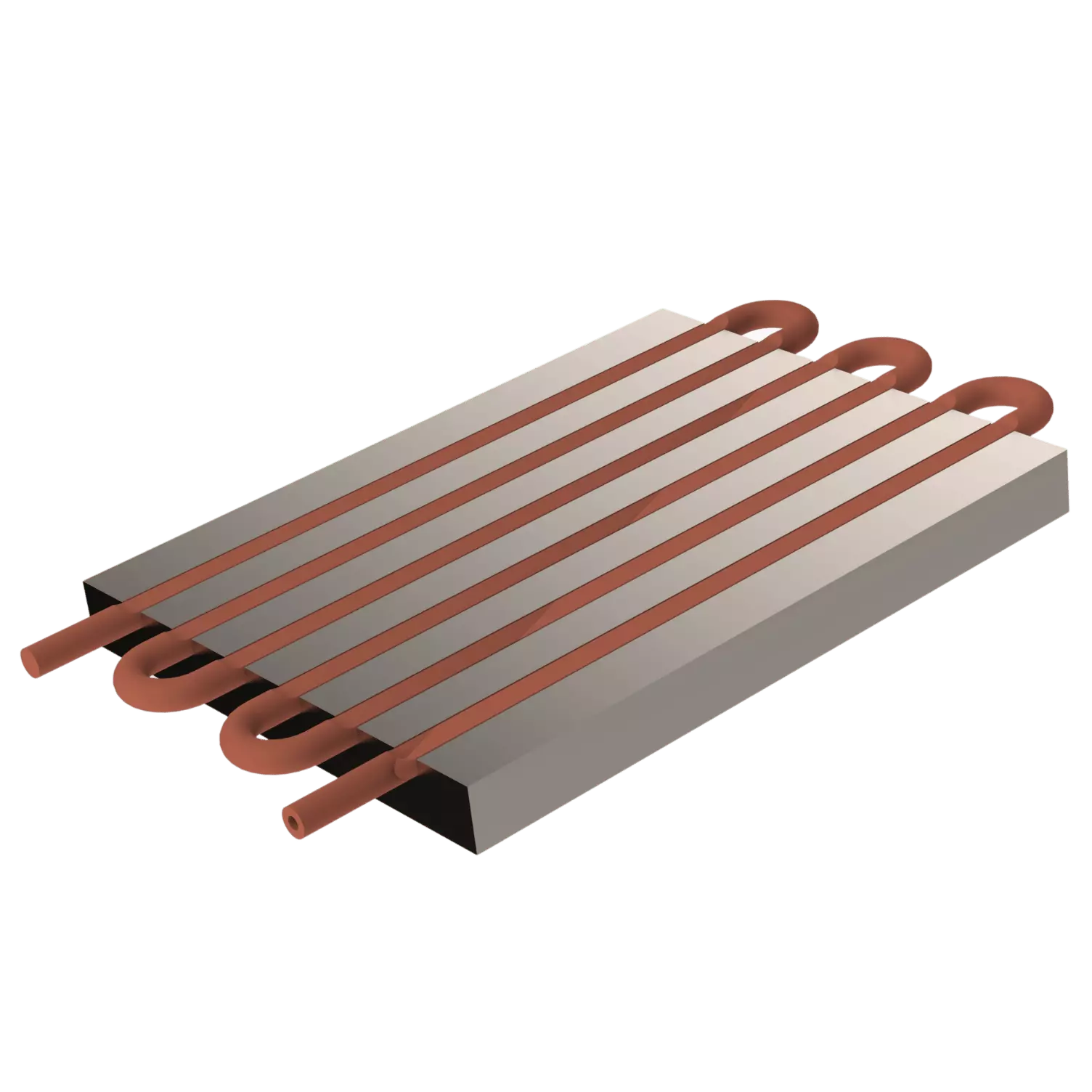
3D of tube liquid cold plate
Gun drilling cold plate
Gun drilling assembled cold plates offer benefits but have design constraints, especially on cooling surface flexibility due to straight-line liquid paths. This limits cooling efficiency for intricate applications. Manufacturing plates longer than 500mm with this process is challenging in terms of accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, their connectors are leak-prone, potentially harming the components they cool. These challenges underscore the necessity for innovation in the design and production of these cold plates.

3D of gun driling cold plate
Brazed cold plate
Brazed cold plates are constructed from components that are brazed into a solid unit, a process that can be costly and skill-intensive. The expensive equipment, such as vacuum furnaces costing over €1M, adds to costs, as does surface treatment and maintenance. The 8-hour brazing cycle is long and allows only batch production, with size constraints affecting productivity. Moreover, any brazing defect can pose later service risks. These factors highlight the challenges in the cost, design, production, and safety of brazed cold plates.
Every cold plate type offers its own advantages and challenges. Grasping these is vital when seeking answers to previously mentioned issues. In the following section, we will delve into friction stir welding, an emerging technique that holds promise in addressing these prevalent industry hurdles.
Friction stir welding: a promising solution
As manufacturers tackle the urgent issues in cold plate production, innovative solutions are surfacing. Friction Stir Welding (FSW), a solid-state joining technique, stands out as a promising method, bringing numerous advantages to cold plate manufacturing.
Understanding Friction Stir Welding
FSW is a process that uses a tool to generate frictional heat and mechanically stir materials together. The heat generated makes the materials malleable and allows them to merge without melting, forming a high-strength, high-quality weld upon cooling.

Advantages of Friction Stir Welding for cold plate assembly
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) stands out as a pioneering technique in the realm of cold plate production, offering significant advantages over traditional welding methods. At the forefront of its benefits is its impeccable integrity; the FSW method ensures a 100% leak-free outcome, a testament to its solid-state process which eradicates any porosity issues. When it comes to cost considerations, FSW emerges as a clear frontrunner, being 2 to 10 times more economical than established approaches like copper tubing, brazing, or conventional welding.

Standard liquid cold plate: 200x50x20mm
Welding time: 3min

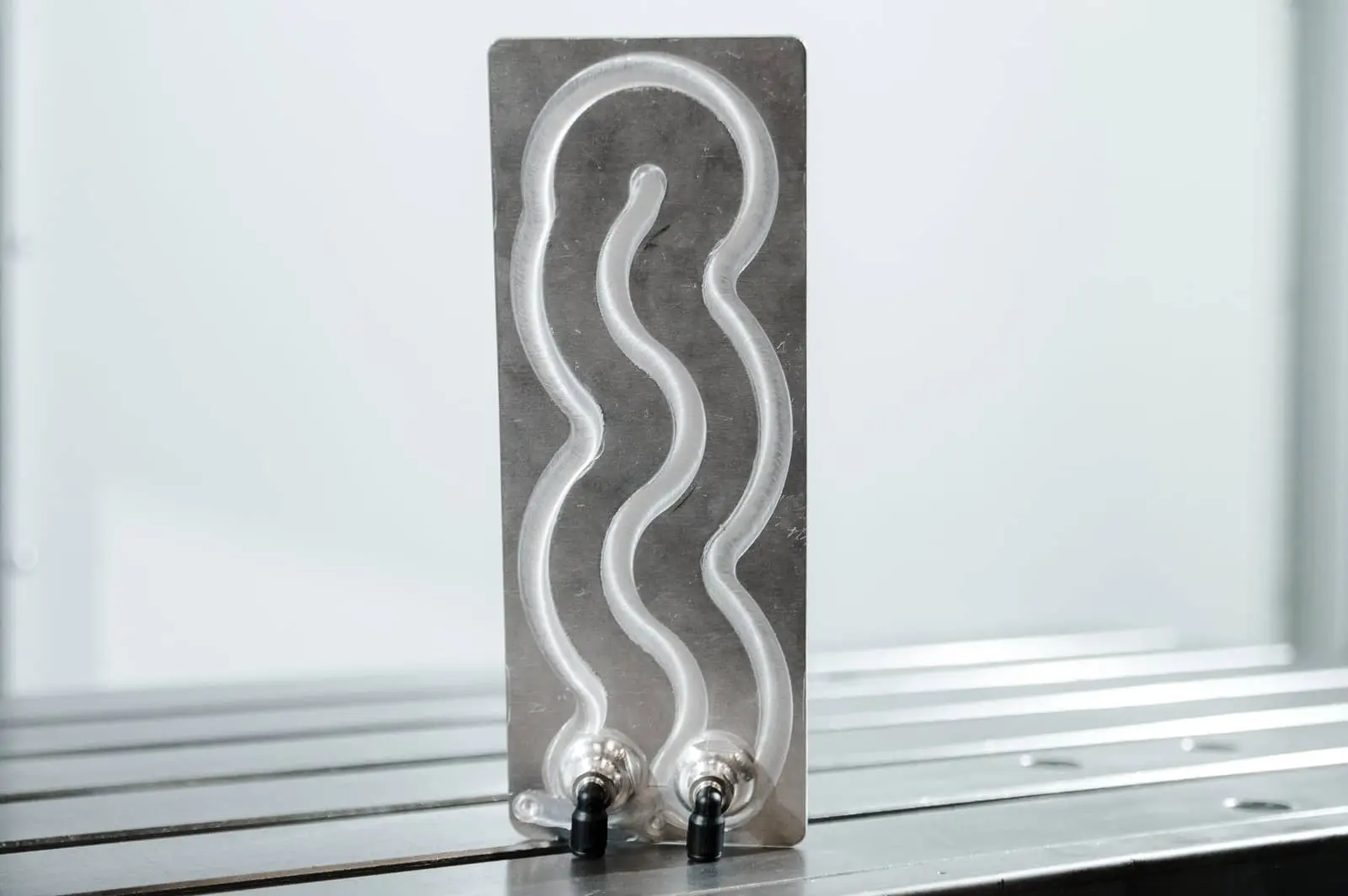
Standard liquid cold plate: 600x10x22mm
Welding time: 5min
In terms of durability, plates produced using FSW showcase exceptional resistance, enduring pressures up to 4300 psi (or 300 bar) without necessitating any post heat treatment. Designing with FSW is a straightforward endeavor; manufacturers can readily access free design guidelines or even request a piece analysis for more detailed insights. The thermal performance achieved using FSW is unparalleled, primarily due to the access it provides to high thermal conductivity materials like AA1050 and copper. This, combined with its easy design attributes and metallurgical junction, ensures superior heat management.
To know more about liquid cold plate welded by FSW, watch now our video about it!
One of the standout features of FSW is its efficiency, reflected in its notably short lead times. The entire manufacturing process can be seamlessly integrated into one’s CNC, and its user-friendly nature means that a mere two days of training can equip an individual to harness its full potential. All in all, FSW is revolutionizing cold plate production, simplifying the intricacies while bolstering efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
FSW solution applied to pain points
FSW impact on liquid cold plate pain points
In addressing the pain points of cold plate manufacturing, Friction Stir Welding (FSW) emerges as a transformative solution. This technique generates a uniform, high-quality weld seam that drastically reduces the risk of leaks, ensuring product integrity and decreasing the chances of operational setbacks and subsequent expenses.
Watch now our video about thin liquid cold plate to understand why le FSW provides 100% sealing for cold plate.
One of FSW’s standout features is its ability to preserve the original thermal properties of materials, since it does not melt them. This preservation enhances the final product’s thermal performance, potentially doubling the thermal management efficiency in cold plates.
Moreover, the strength of cold plates benefits from FSW’s high-strength, void-free weld, augmenting their durability and extending the lifespan of the cooling systems in which they’re incorporated. On the economic front, FSW proves to be a game-changer. Its potential for automation reduces labor costs, while its minimization of waste cuts down on material expenses. The technique’s repeatability and quality further curtail costs linked to rework and warranty issues. Intriguingly, FSW stands out as being 2 to 10 times more cost-effective than traditional methods such as copper tube, brazing, or conventional welding. As industries aim for ambitious targets like a tenfold cost reduction, FSW confidently positions itself as a pivotal player in achieving this objective.
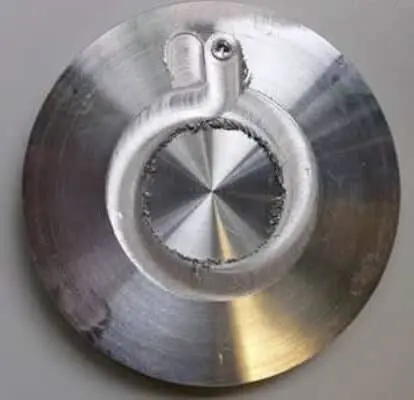

Circular liquid cold plate: cover made in 6061-T6 and housing in 5754-H111
Welding time: 1min
Download more information
The adoption of Friction Stir Welding not only affects the design of your cold plate but also its manufacturing process, cost, and the safety of your teams.
To learn more about these topics, download our white paper dedicated to the challenges associated with cold plates!

