Revolutionizing FSW Welding: FSW Automation Strategy
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, friction stir welding (FSW) stands out as a revolutionary technique for assembling materials. Known for its ability to produce robust and high-quality welds, this process is particularly valued in the aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries. However, despite its numerous advantages, optimizing production and reducing costs remain significant challenges.
The FSW automation welding operations represents a promising solution to these challenges. By automating this process, companies can not only improve the precision and consistency of welds but also increase production capacity and reduce the need for skilled labor.
This article explores various automation strategies for FSW welding through a concrete case study: the manufacture of an aluminium cold plate. This component requires four distinct manufacturing steps, from initial cutting to complex machining, including welding and post-welding finishing.
We will examine how, starting from a simple production of 50 parts per year, it is possible to move to medium and high volumes up to a fully automated production of more than 15 000 parts per year.

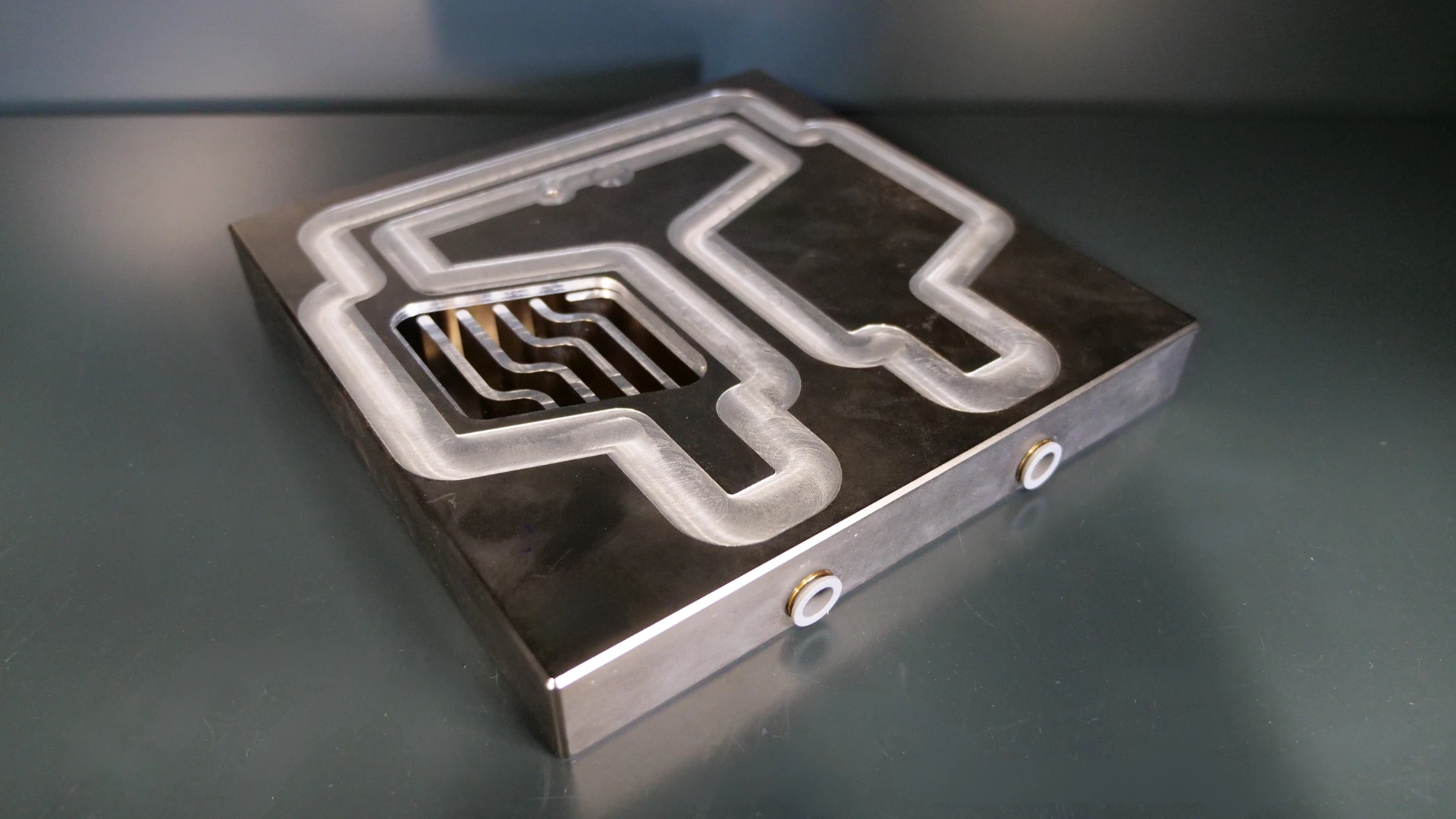
Manufacturing steps in our case study: aluminium cold plates
In this case study, we focus on the manufacture of an aluminium cold plate, an essential component used in various industrial applications for the efficient cooling of components. The manufacture of this cold plate involves four crucial steps, each contributing to the quality and functionality of the final product:

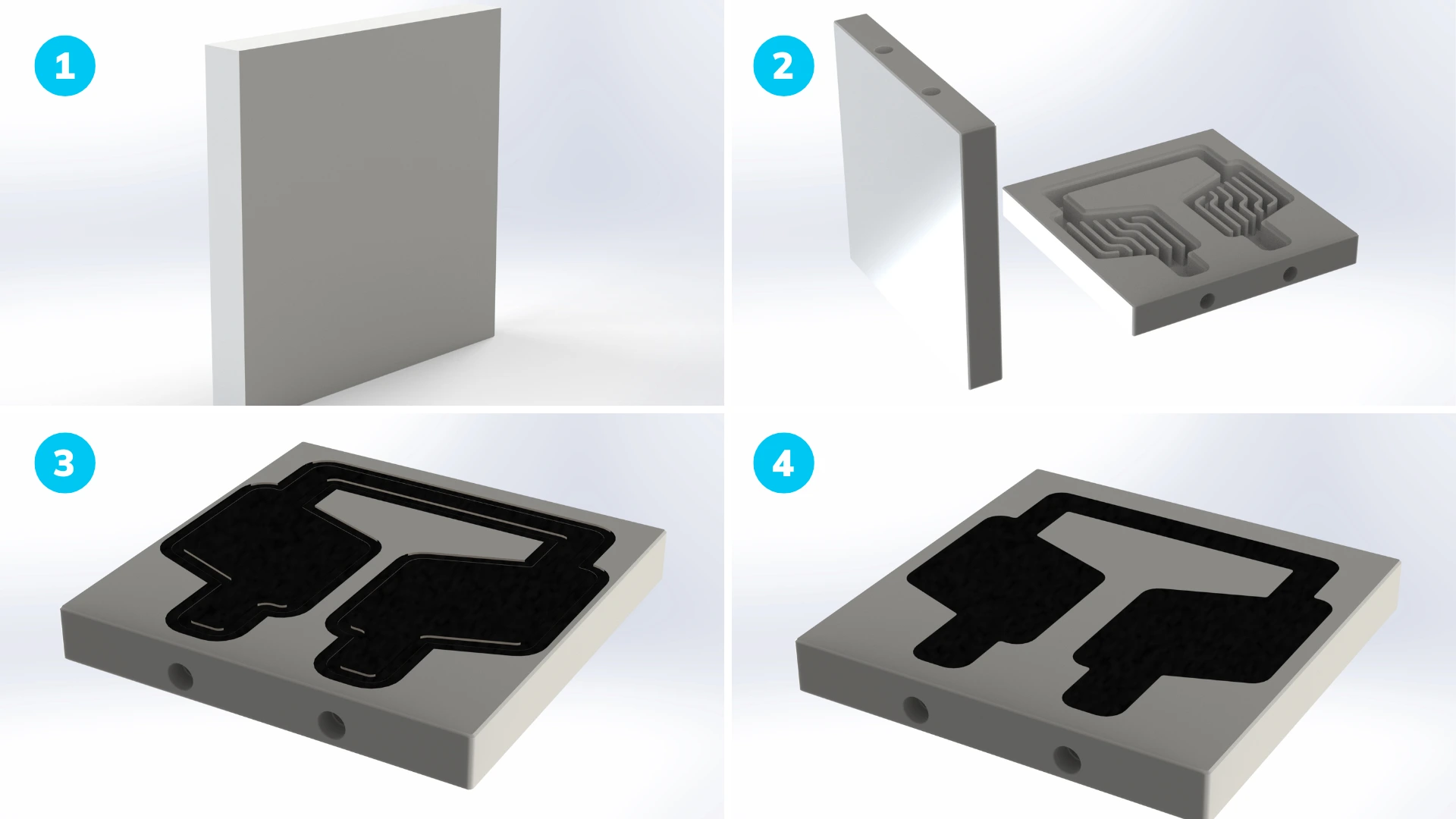
By following these four steps, the production of aluminium cold plates achieves a high level of precision and quality. Each step is optimized to ensure process efficiency and the performance of the final product, laying the foundation for increased FSW automation as production volumes grow.
Production scenarios based on the volume of FSW-welded parts
To meet varying production needs, different automation solutions are considered based on production volume. These scenarios range from low-volume, full manual production to mass production with fully automated cells. Here are some examples of scenarios.
Low-volume production with a machining center and FSW head: annual production of 50 parts
Low-volume production relies on fully manual operations. A machining center equipped with an FSW welding head is used to manufacture cold plate.
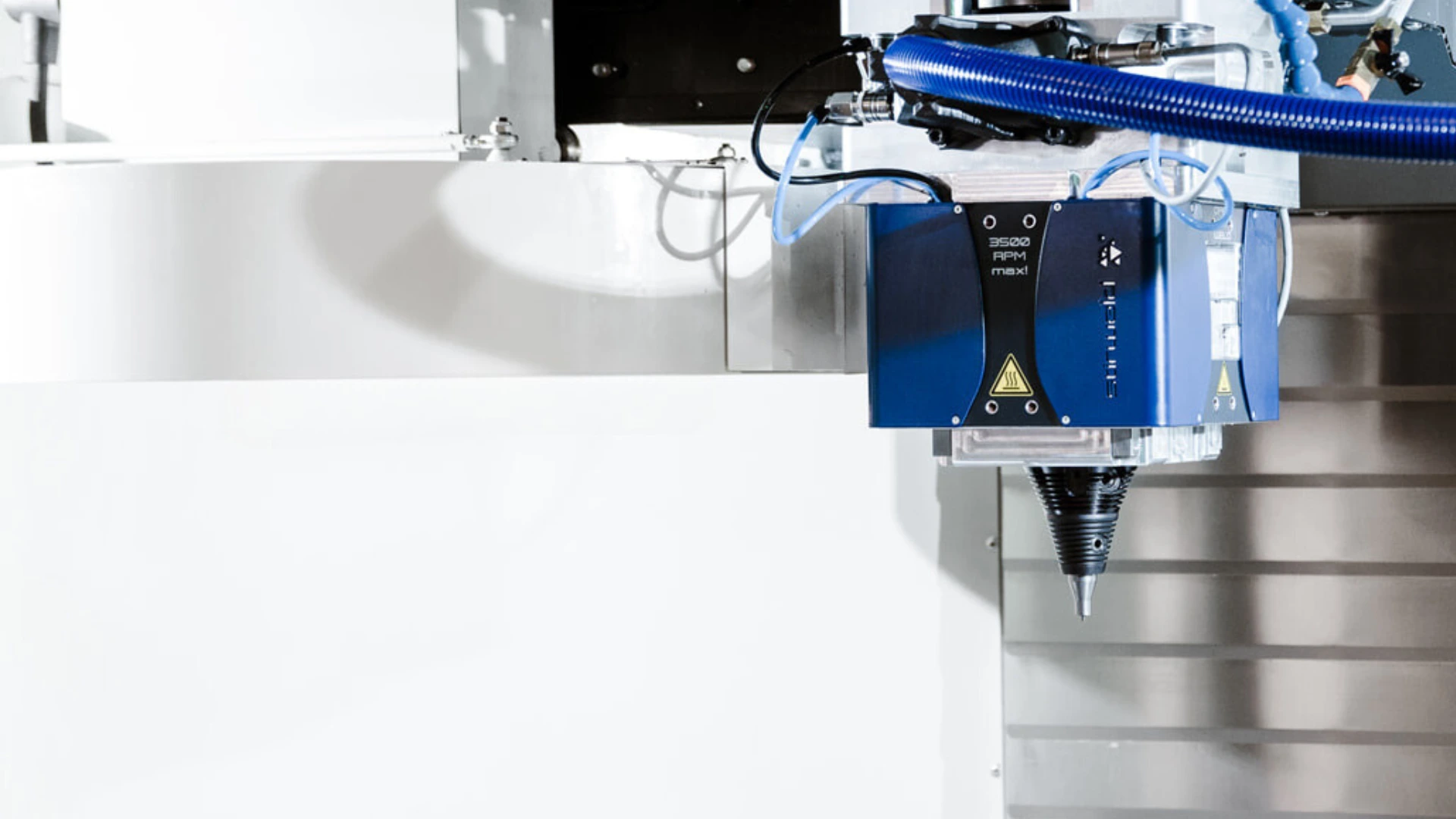
| Advantages | Limits |
| – Flexibility: adaptable to different designs and quick modifications. – Low initial cost: no need to invest in expensive automation systems. | – Lower efficiency: manual production is lower and dependent on operator speed. – Variability: risk of variability in part quality due to human intervention. |
Medium-volume production with an automatic FSW head changer
Scenario 1: up to 5000 parts per year
This solution involves using a machining center equipped with an automatic FSW head changer to quickly switch between machining and welding:
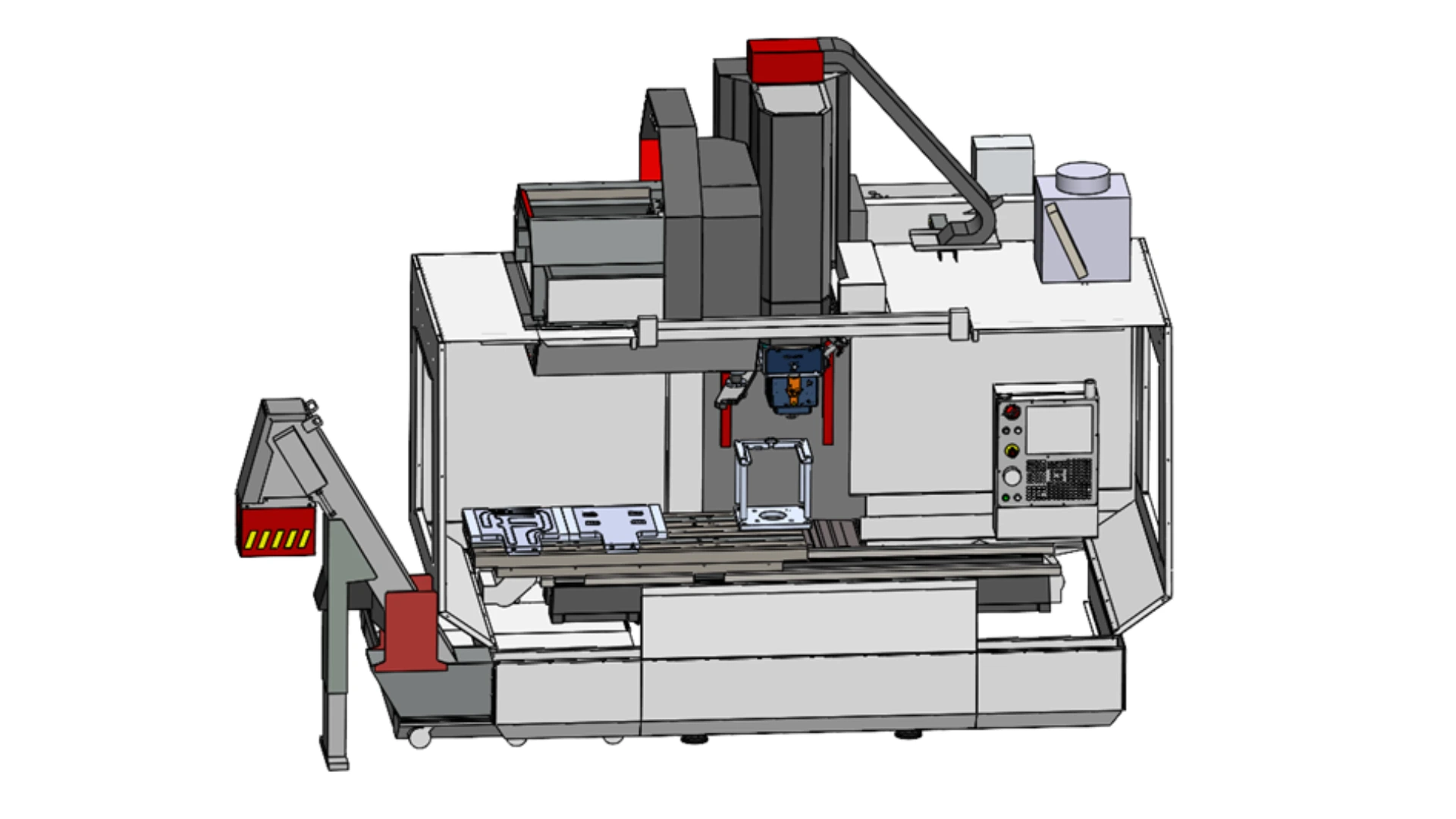
Scenario 2 : up to 10000 pieces per year
Here, two machining centers are used: one equipped with an FSW welding head with an automatic head changer and the other dedicated solely to machining. The machining and welding processes are separated, allowing for optimization and specialization of each machining center.
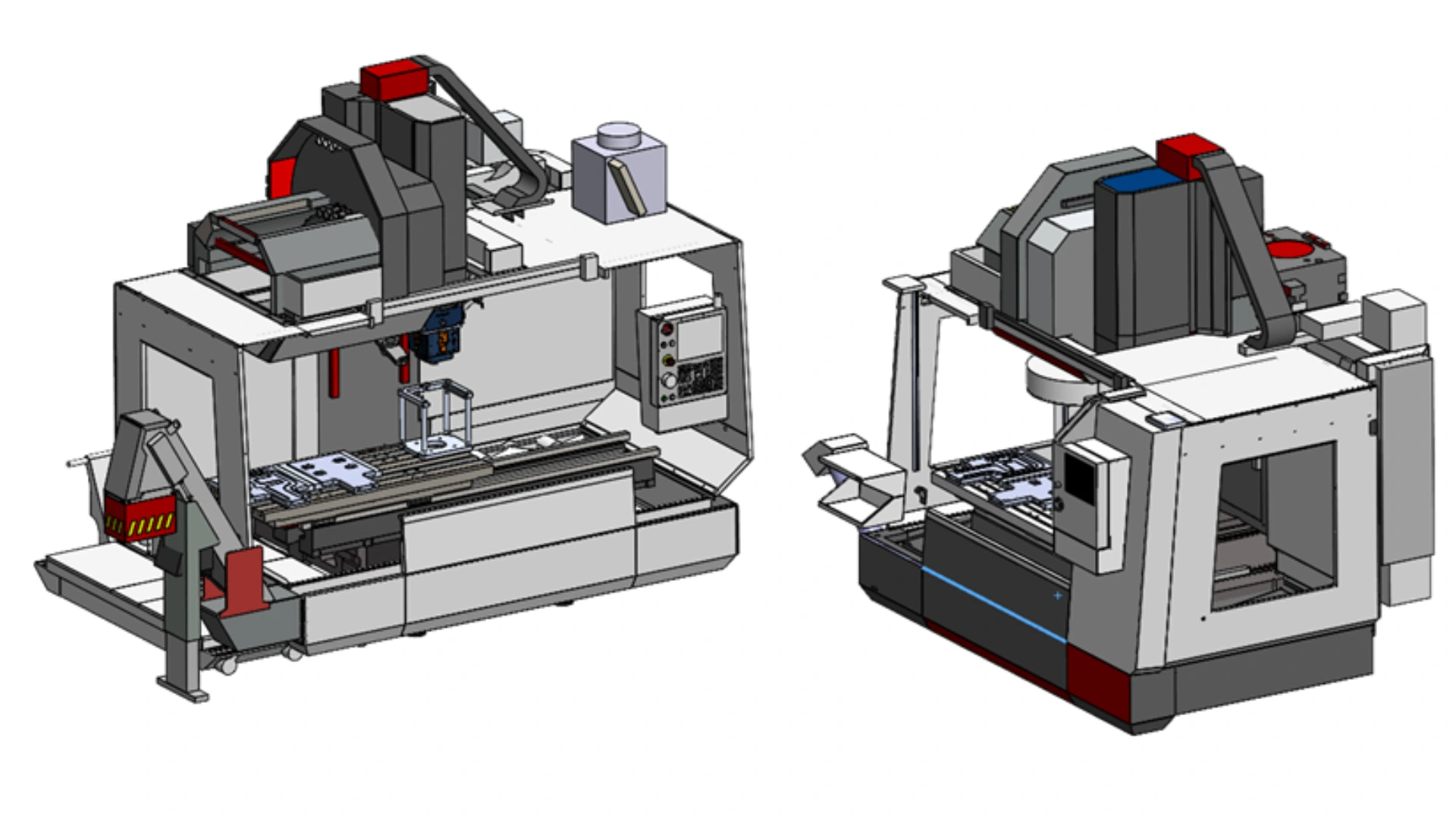
| Advantages | Limits |
| – Productivity : significant increase in production volume by separating tasks – Reduced bottlenecks: each machining centre can operate independently | – Higher cost : higher initial investment due to the purchase of two machining centers. Additionnaly, an FSW welding head can be mounted on any machining center, allowing retrofitting of an old machine to reduce costs! |
Scenario 3 : up to 15 000 pieces per year
For this scenario, three machining centers are used, with two dedicated to simultaneous machining to double production and one dedicated exclusively to FSW welding with an automatic head changer.
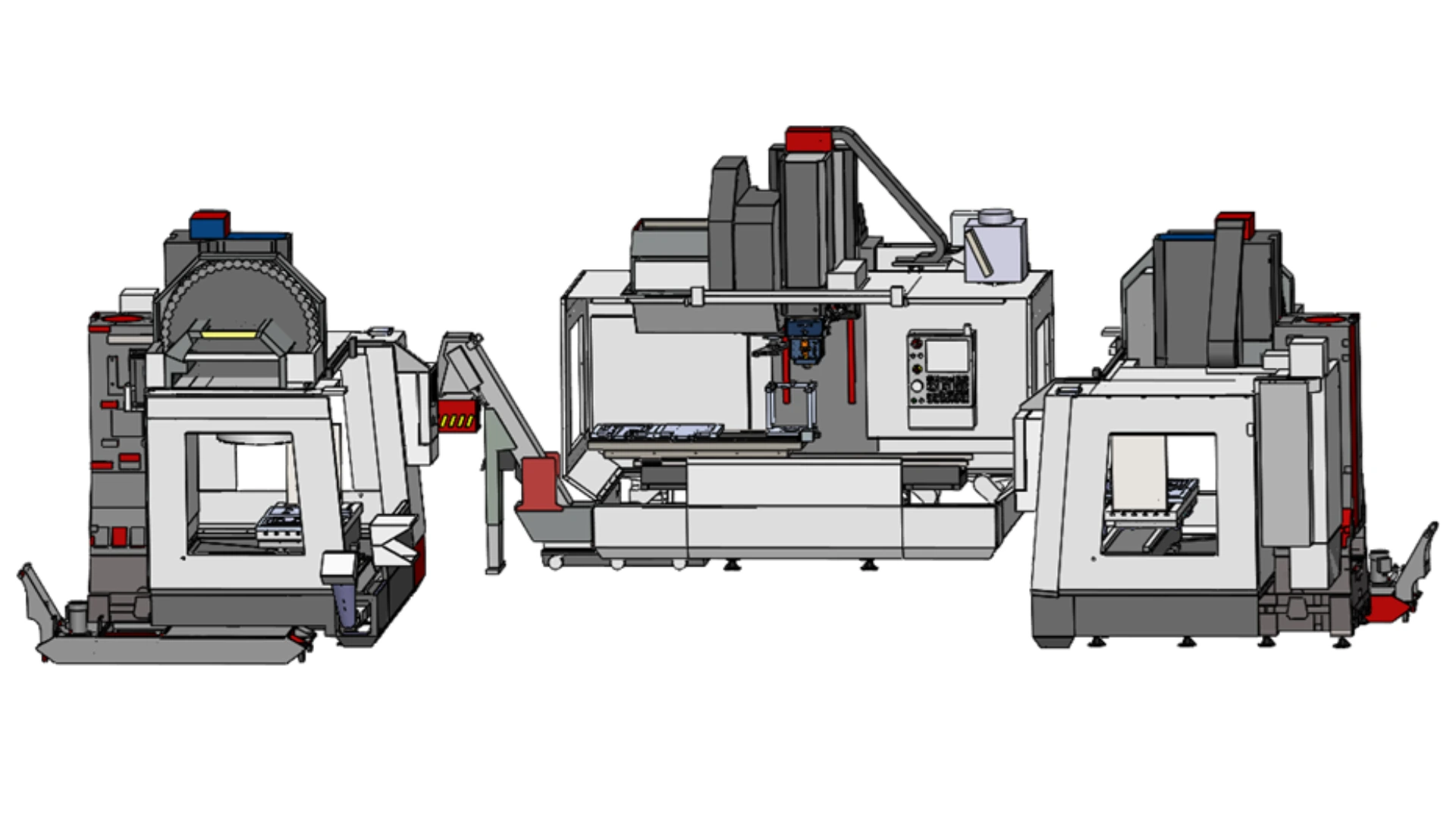
| Advantages | Limits |
| – High production capacity : reduced machining times using two machining centers simultaneously. – Spezialization: a center entirely dedicated to FSW welding ensures consistent quality. | – Complexity: coordination needed between multiple machining centers. – High cost: initial investment and equipment maintenance costs. |
FSW Automation: Innovative solution to optimize your production time
A new scenario is also possible for high-volume production: a rotary table. Here, a machining center equipped with a rotary table allows for loading and unloading of parts on one side while the FSW welding operation is performed on the other. For even more productivity, automatic clamping tooling should be used to quickly and precisely secure the parts without human intervention.
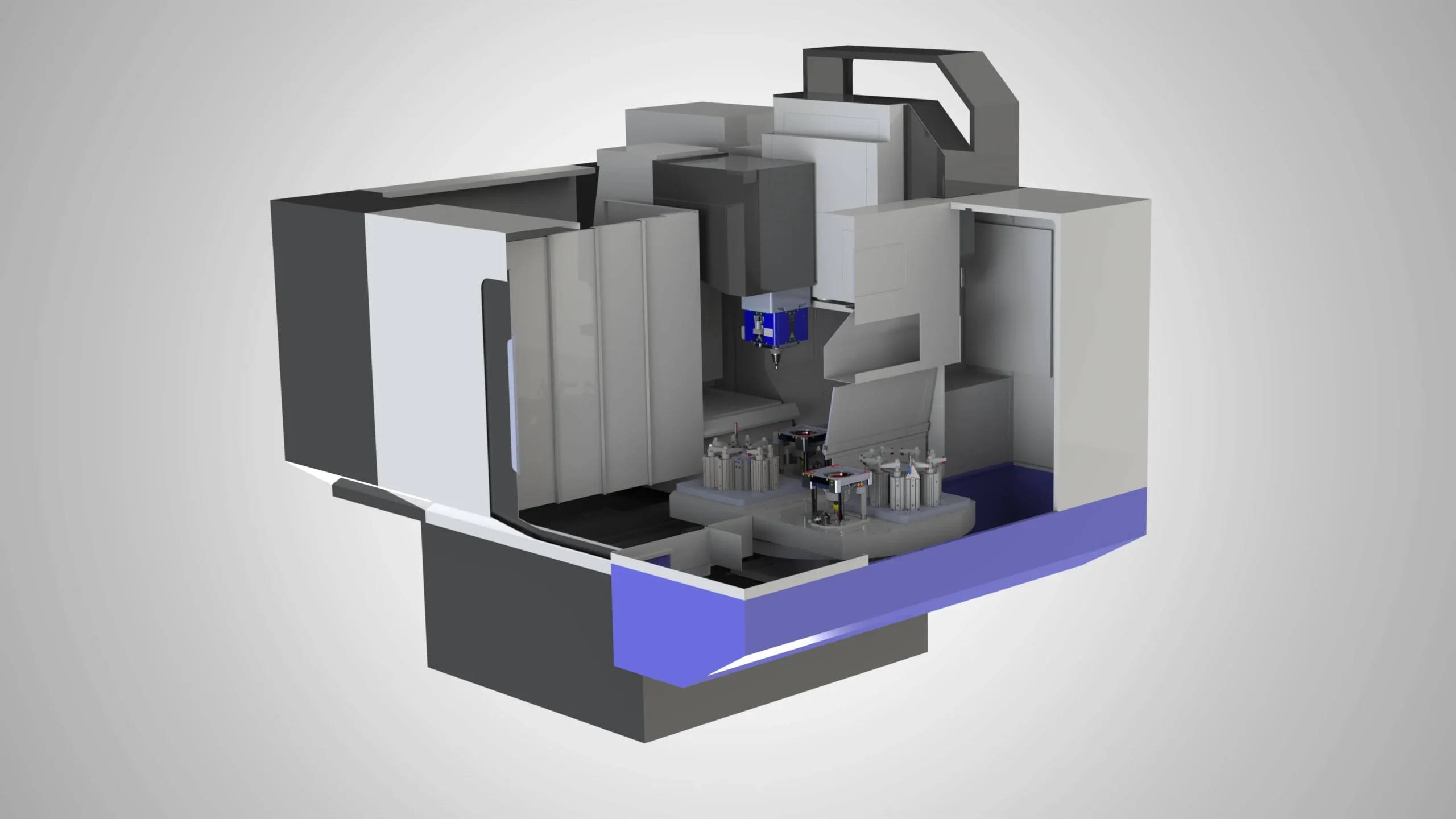
CNC solution for high-volume production.

CNC rotary table: loading/unloading parts on one side while the FSW operation is performed on the other side.

The part is welded using an automatic clamping jig. Then, the milling module removes the flash from the FSW weld (weld cleaning).
| Advantages | Limits |
| – Time savings: simultaneous loading and unloading increase efficiency. – Reduced downtime: the rotary table allows continuous operation without interruption. | – Cost : the rotary table system and automatic tooling represent a significant investment. |
High-volume production with a fully automated cell
With annual production exceeding 15,000 pieces, setting up a fully automated production cell, where robots are used to load and unload parts into different machines, is advantageous. This allows for 100% automated operation, with no operators needed to monitor manufacturing processes.
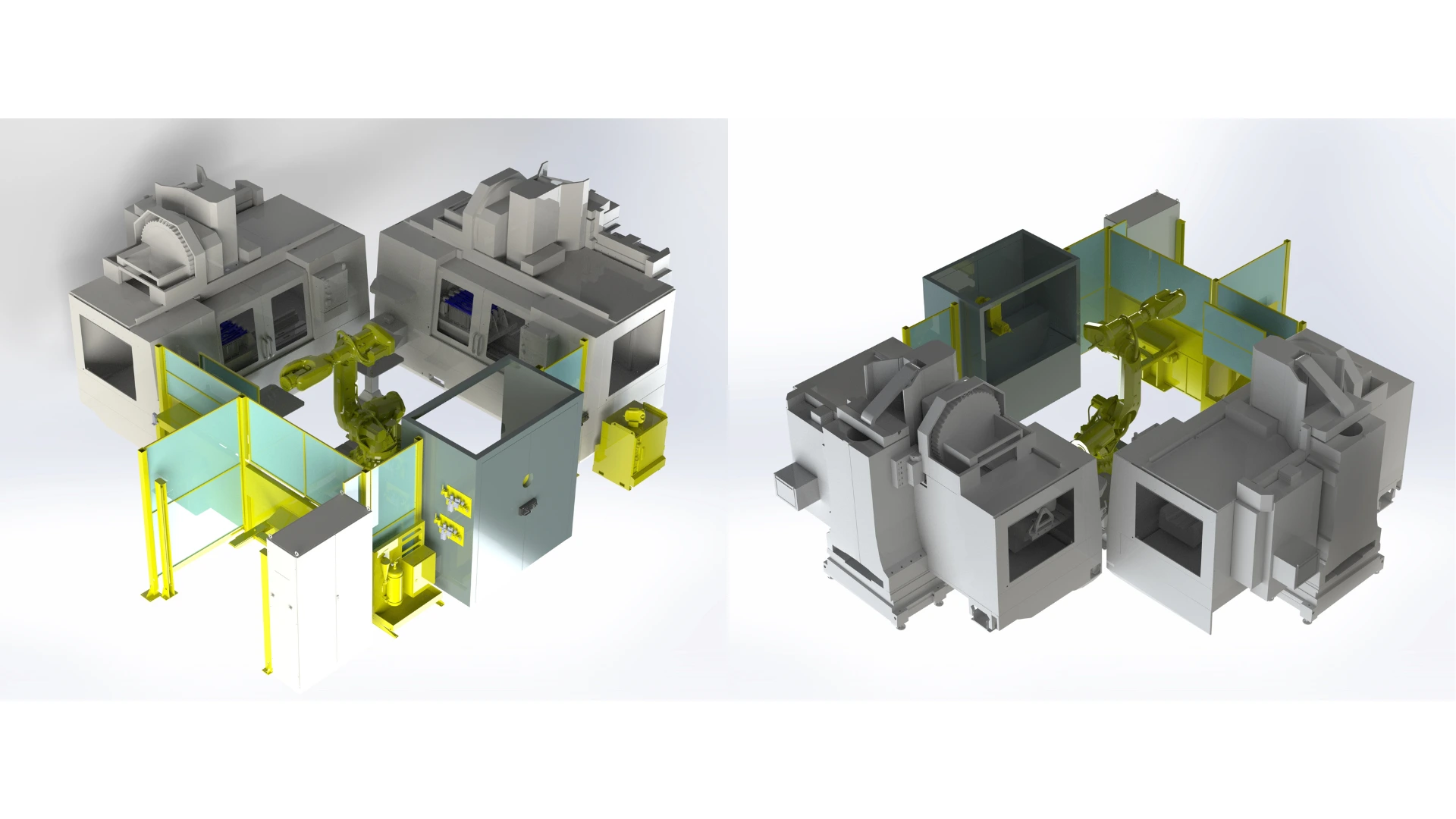
| Advantages | Limits |
| – Maximum productivity: 24/7 operation without human intervention. – Consistent quality: reduced human errors and uniformity of finished products. | – Maintenance : need for specialized personnel to maintain and repair automated equipment. |
These different scenarios show how FSW welding operations can be adapted and automated based on production needs. The evolution from manual solutions to fully automated systems allows companies to efficiently meet growing demands while optimizing quality and profitability.
Automating friction stir welding (FSW) operations offers exceptional opportunities to optimize production, improve weld quality, and meet increasing market demands. By analyzing different production scenarios based on volume, we have explored solutions ranging from manual craftsmanship to fully automated systems capable of operating without human intervention.
Each level of automation presents its own advantages and challenges, but all share a common goal: increasing efficiency and productivity while maintaining high-quality standards. Whether you produce 50 pieces per year or achieve massive production volumes of over 15,000 pieces, there are solutions tailored to each specific need.
Are you considering automating your FSW welding processes?
Our experts are available to assist you in this endeavor. We offer a personalized evaluation of your needs and help you choose and implement the best technological solutions for your business.

