Thermal performance: why FSW is a game-changer in the industry
In all electronic or mechanical systems exposed to significant thermal loads, the ability to dissipate heat quickly is a critical issue. And when it comes to designing efficient, sealed and durable components, the way materials are joined makes all the difference.
This is where Friction Stir Welding (FSW) stands out. Much more than a simple welding process, FSW is now a high-performance thermal joining technology.

FSW – a solid-state joining process
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is a solid-state welding process, meaning the materials are never melted during assembly.
A rotating tool slides against the parts to be joined, generating localized heat sufficient to soften the metal without melting it. The tool pin then stirs the softened material to create a continuous metallurgical bond between the parts.
The result:
And this continuity is the key to optimal heat conduction.
Welding and thermal transfer – what you need to know
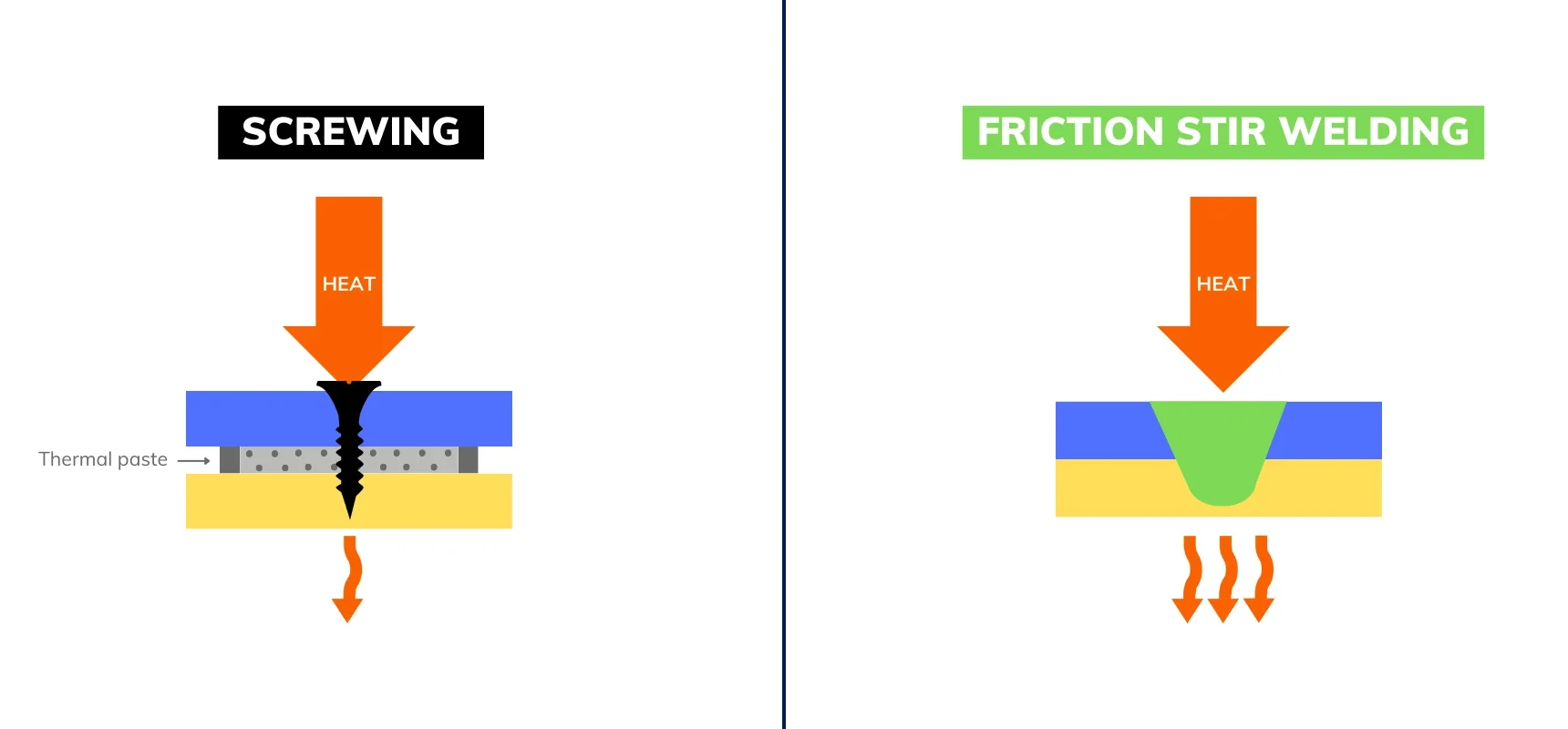
Efficient heat transfer is based on a simple principle: heat flows better through a homogeneous material than across different materials. In other words, every interface (material discontinuity, air gap, thermal paste, solder, or screw) creates a drop in performance.
In a screwed assembly, for example, the interface between the two parts is filled with thermal paste. Even with the best pastes, thermal conductivity remains far below that of solid metal.
The only way to optimize heat flow is to eliminate that interface entirely.
That’s exactly what FSW enables.
How does FSW improve thermal performance?
Seamless heat conduction
FSW creates a continuous metallurgical joint. Instead of two parts in contact, you get a single homogeneous part through which heat can flow freely.
This is what fundamentally sets it apart from screwing or even brazing (where filler metal acts as a third, often less efficient, conductor).
Welding highly conductive aluminium alloys
FSW opens the door to highly conductive aluminium alloys (1xxx series). With thermal conductivity above 220 W/m.K, they are ideal for heat dissipation – but almost impossible to weld using fusion-based techniques.
With FSW, you can weld a 1050 cover to a 6061 base, combining thermal performance and mechanical strength. This is the only technology today that makes this possible – with no filler metal and no compromise.

Aluminium and copper: a high-performance thermal joint, finally possible

Copper has even better thermal conductivity than aluminium. FSW makes it possible to weld aluminium to copper – something previously very difficult to achieve without introducing defects or corrosion.
This allows you to reinforce critical thermal areas with copper while using aluminium for the rest of the part — a major gain in weight and cost.
These hybrid assemblies require careful management of galvanic corrosion risks. Stirweld supports its customers with design guidance from the very first steps.
Applications in demanding industrial sectors
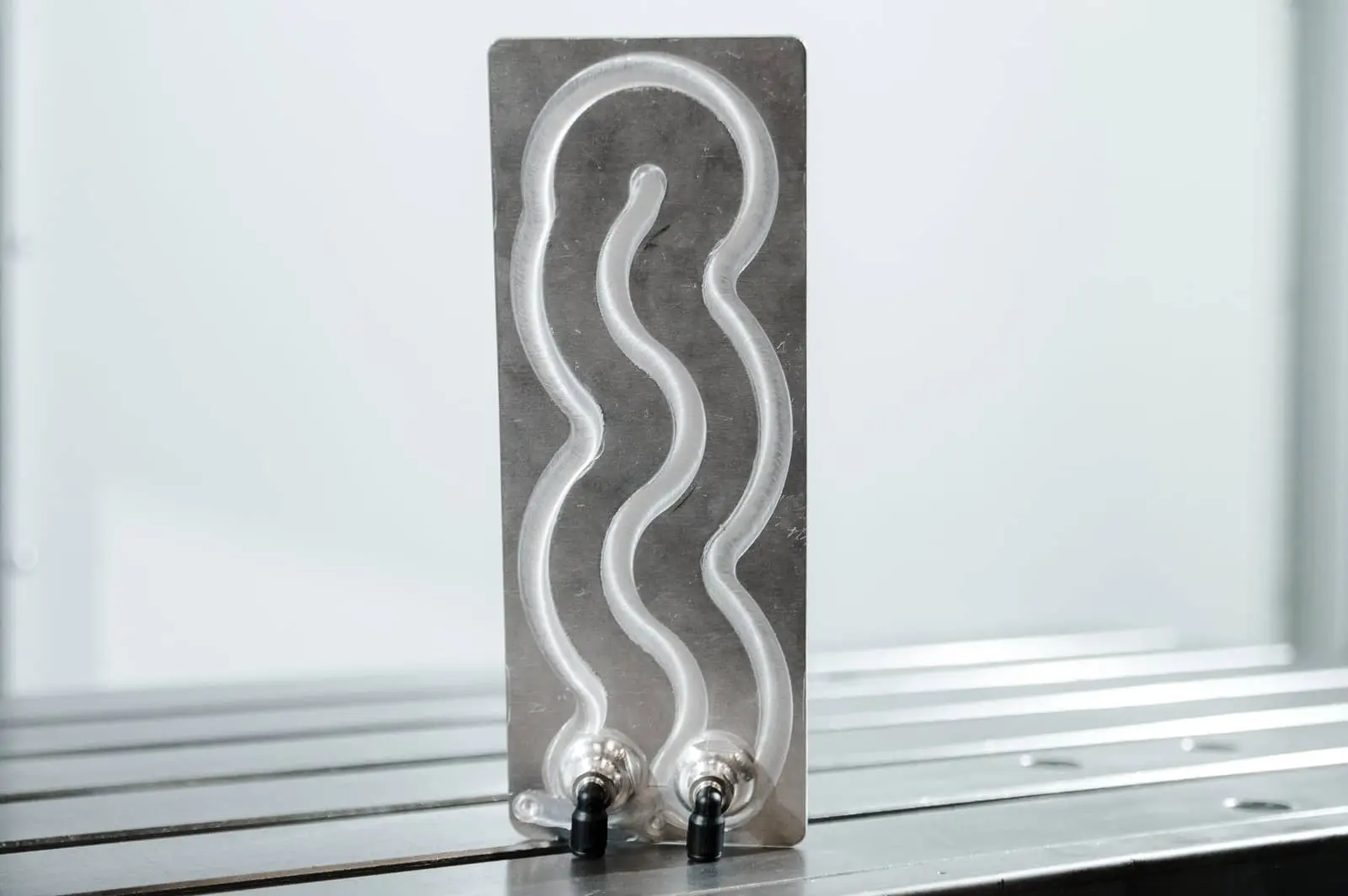
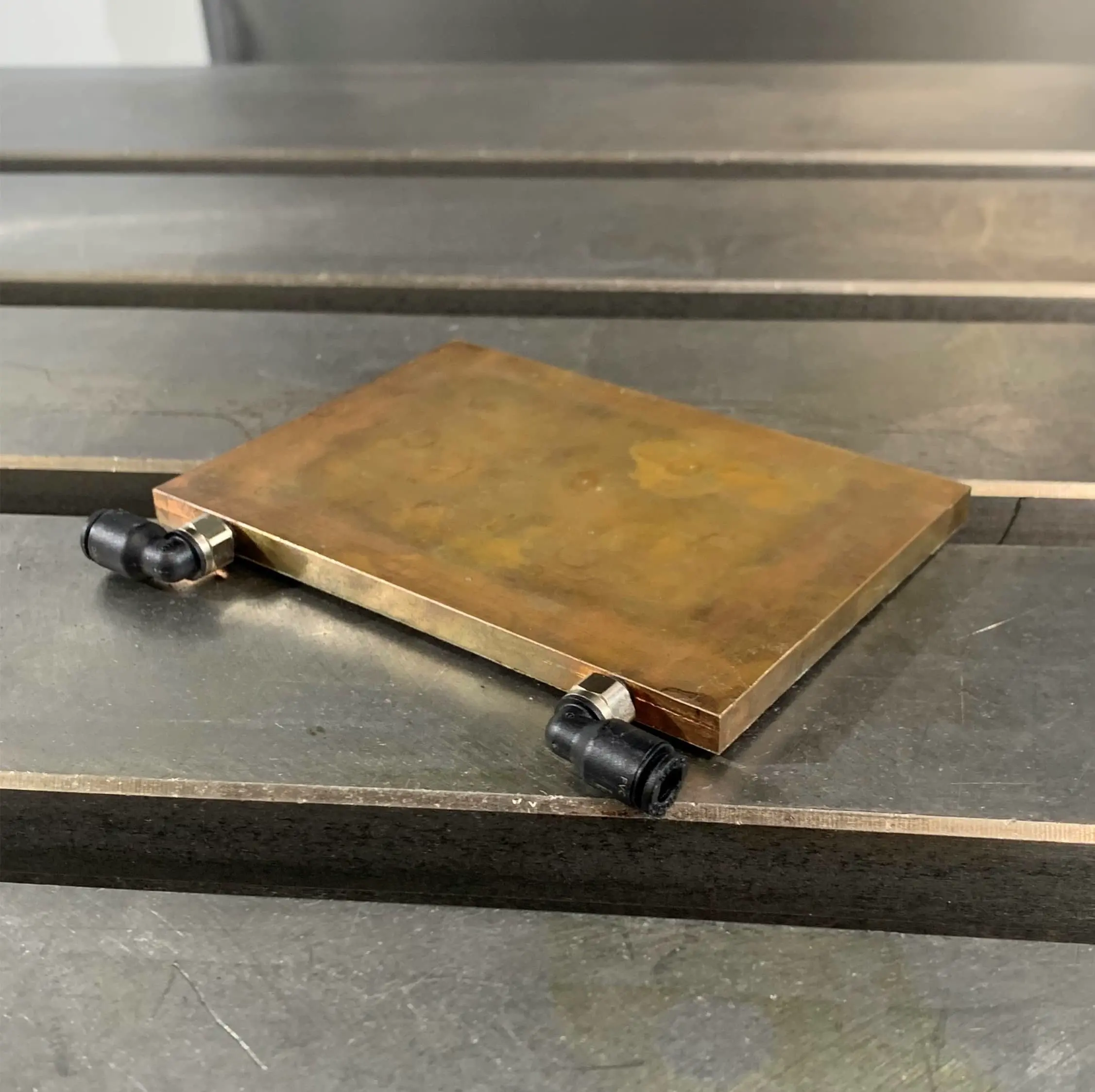
FSW-welded cold plates
Among all FSW applications, cold plates are perhaps the most iconic. The process meets the demanding requirements of this type of component — thermally, mechanically and industrially.
With Friction Stir Welding, you get:
Want to go further? Download our white paper: Overcoming cold plate manufacturing challenges.
It provides a complete analysis of thermal, mechanical and production constraints — and how FSW solves them.




Cast aluminium parts
With the rise of cast aluminium in sectors like automotive (for example in cooling housings), new welding solutions are needed. FSW makes it possible to weld cast aluminium without compromising mechanical integrity.




FSW design: key rules for thermal performance
To fully benefit from FSW’s advantages – sealing, strength, thermal efficiency – specific design rules must be followed for cold plate welding.
Spacing between cooling channels
Internal channels carrying coolant must be spaced far enough apart to ensure reliable welding between them.
The closer the welds, the thinner the residual material between channels — which increases the risk of wall distortion during FSW.
The minimum spacing depends on welding depth and tool diameter, and must be considered early in the design phase.

FSW RESSOURCE
11 rules for perfect compatibility with FSW
Learn how to optimize your designs, reduce costs and achieve stronger, more durable welds.
To obtain your free FSW resource, you just need to fill in a simple form.

Support step under the cold plate cover
To withstand the vertical force applied by the FSW tool during welding, a support area (or “step”) must be added beneath the cover.
Its minimum width depends on the welding depth and tool diameter, but this is essential to guarantee joint stability and avoid local distortion.

In summary – what FSW brings to your thermal performance
Working on a demanding thermal project?
Our experts support you in the design and production of FSW-welded cold plates.

